TEACHER’S GUIDE | |
MIDI INSTRUMENT SURVEY PROJECT | |
NSME: | 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
GRADE SCHOOL | GRADE SCHOOL – HIGH SCHOOL |
CLASS TIME | 2 ONE-HOUR PERIODS |
REQUIRED MATERIALS:
Computer with Mixcraft
Headphones or Monitors
MIDI Versions of Children’s Songs (Additional Material Download)
Copies of the MIDI Instrument Survey Student Guide (Additional Material Download)
SUGGESTED MATERIALS:
MIDI keyboard
Sheet Music to Transcribe (For Older Students)
Further Reading Materials
OVERVIEW: MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a digital system that allows certain music hardware and software to communicate. Computer software such as Mixcraft commonly uses MIDI for composing, arranging, or recording music. With MIDI, Mixcraft users can program, note by note, a melody or a drum beat and can quickly assign virtual instruments for play back.
This workflow enables composers to experiment with various instrumental arrangements even after a melody has been written. Additional MIDI capabilities include automation, transposition, and even notation. Advanced lesson plans might explore these functions. Because MIDI is an integral component of computer music and of digital music production, students need to have a solid understanding of how to use MIDI in a computer environment. This lesson guides students through the process of using MIDI to work on imported pieces, to compose melodies, and to assign virtual instruments for play back.
LESSON: For grade school and middle school projects, several MIDI-transcribed versions of popular children songs are included in the “Additional Material Download.” Students will import these MIDI files into Mixcraft and use Mixcraft’s virtual instruments to arrange the melodies. For younger students, a lesson focused on instrument identification can benefit from the workflow and setup in the following task: Quickly assign different timbres or instruments to a single MIDI melody and ask students to identify each instrument. For high school classes, students can either compose an original melody using MIDI or program sheet music into a MIDI format. In both contexts, students will gain an understanding of MIDI and learn its application in both music composition and arrangement.
SKILLS GAINED
Understanding of MIDI
Understanding Virtual/Software Instruments
MIDI Programming
MIDI Editing
ACTIVITY
Research instrument families. The Hornbostel–Sachs classification system is a respected catalog of musical instruments that are sorted according to structural and functional criteria.
However, depending on the age of your students, it may not be necessary to focus on the minute differences between instruments: instead, highlighting large and general characteristics across instrument families is suitable for this lesson. Several examples are listed below:
Brass family
Woodwind family
String family
Percussion family
To begin the lesson, launch Mixcraft and open File>Set Project Default Settings. Set the New Project window Instrument Tracks to 1 and click OK. Now click File>New Project.
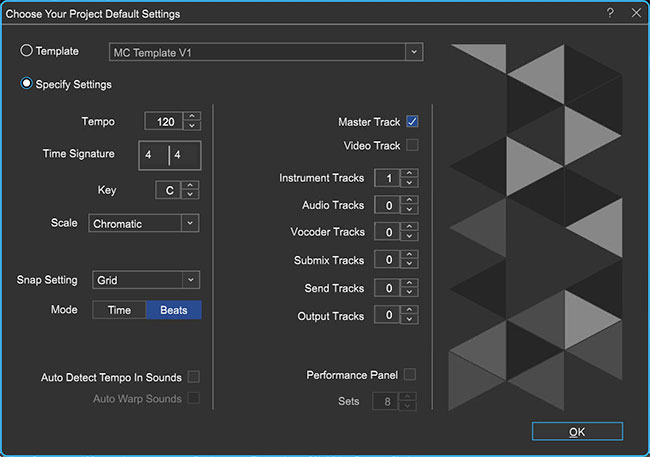 Once the New Project window has loaded, remove any audio tracks, and set the Instrument Tracks field to 1.
Once the New Project window has loaded, remove any audio tracks, and set the Instrument Tracks field to 1.Import a MIDI file of a song from the “Additional Materials Download Area” into Mixcraft. Simply, drag and drop the file onto Mixcraft’s Timeline or onto the virtual instrument track. A Mixcraft prompt window will give users the option to change the master tempo to the tempo in the MIDI file. Select “Yes” for now.
 Users will be prompted with the option to change the master tempo. Select “Yes” for now.
Users will be prompted with the option to change the master tempo. Select “Yes” for now.A MIDI region of the song will now appear on a virtual instrument track. Lines on the region refer to note duration and pitch: higher lines on a vertical axis have higher pitch while longer notes on the horizontal axis represent duration.
 A MIDI representation of “Eency Weency Spider.”
A MIDI representation of “Eency Weency Spider.”Before playing back the newly imported song, assign a virtual instrument to the virtual instrument track. Click the “keyboard” icon on the virtual instrument track. A new window will appear.
 Click the keyboard icon on the virtual instrument track to assign virtual instruments.
Click the keyboard icon on the virtual instrument track to assign virtual instruments.Browse Mixcraft’s virtual instruments by instrumental category. Brass, guitar, wind, and keyboard sounds are readily available – simply double-click on a sound to assign it to the virtual instrument track.
 Mixcraft’s instrumental categories.
Mixcraft’s instrumental categories.Play back (hit the master play button or space bar) the melody and notice how the selected virtual instrument is now “playing” the MIDI song.
With this basic setup, educators can construct multiple lesson plans that emphasize different attributes of instruments and their respective instrumental families. Here are some simple lesson plans for students:
Describe a particular instrument family (say the “brass family”) and ask students to find a brass sound.
Assign different instruments to the same melody, one at a time, and ask students to describe the timbre (“tone” or “color”) of each instrument.
Browse through Mixcraft’s synthesized sounds and compare these digital emulations to their acoustic counterparts.
Duplicate the MIDI melody and assign different instruments to it. Combine and mix down timbres for more complex and rich tone colors.
Assigning a pizzicato string sound to the Eency Weency Spider melody.
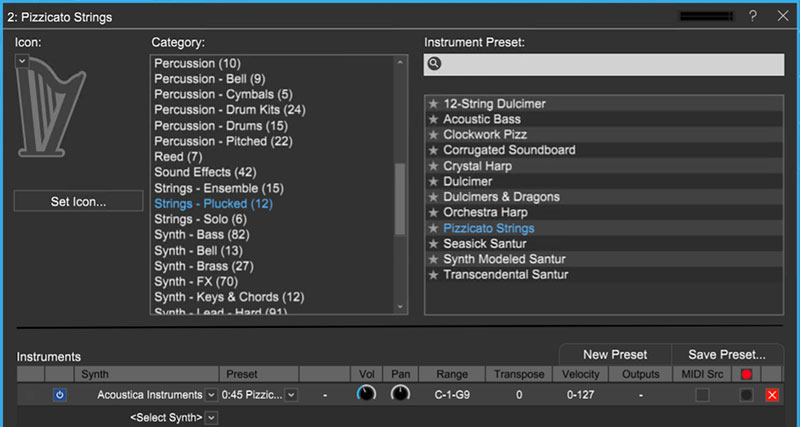 Mixcraft’s instrumental categories.
Mixcraft’s instrumental categories.
Older students can compose original melodies or transcribe sheet music into MIDI format by using Mixcraft’s Piano Roll:
First, create a new virtual instrument track by selecting one from the menu:
Track > Add Track > Add Virtual Instrument track.
Double click on the Timeline area that corresponds to the new virtual instrument track. A blank MIDI region should appear and the Piano Roll window should expand from the bottom of the screen.
Select the Pencil tool in the Piano Roll. This tool allows users to “draw” MIDI notes onto the Piano Roll. Notes drawn on the Piano Roll will then appear in the MIDI region on the Timeline as well.
 The Piano Roll Toolbar consists of the pointer arrow, the pencil tool, the paint brush tool, and the eraser tool.
The Piano Roll Toolbar consists of the pointer arrow, the pencil tool, the paint brush tool, and the eraser tool.Users can draw basic melodies or transcribe sheet music onto the Piano Roll.
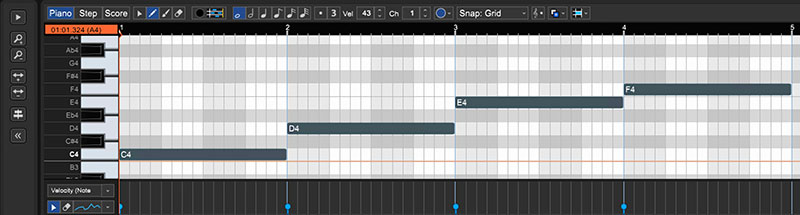 A sample melody in C Major programmed using Mixcraft’s Pencil tool and the Piano Roll.
A sample melody in C Major programmed using Mixcraft’s Pencil tool and the Piano Roll.To tidy up the MIDI notes, quantize them. Quantizing locks each MIDI note to the Piano Roll grid and can also be used to control the duration of each note. To do this, select “Quantize” from the MIDI Editing menu at the top of the Piano Roll window.
In the example above, the notes were then quantized to an “8th note” with the “note endings” option selected.
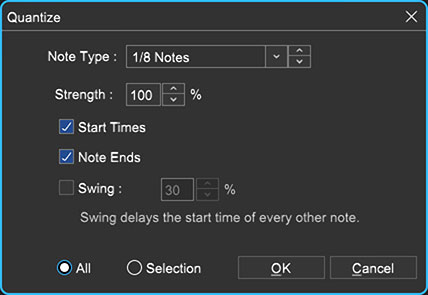 Example settings in the “Quantize” window.
Example settings in the “Quantize” window.
If available, provide sheet music for students to transcribe or allow students to freely compose a short melody using Mixcraft’s Piano Roll. Once the transcription or composition is completed, encourage student to experiment with different instrumental arrangements.
Students can save their MIDI melodies in MIDI format. Simply select the MIDI regions and go to File > Save as MIDI file … These files will now be stored on the computer hard drive and can be exported, imported by different computers or used in new Mixcraft sessions.
After students have explored Mixcraft’s virtual instruments and MIDI functions, they will be prepared for larger, MIDI-intensive projects!
ADDITIONAL LESSON PLANS
MIDI Symphony: A symphony in the classroom? Of course! With Mixcraft you can create an entire symphony with one computer and virtual instruments. Create a lesson plan that explores the elements of the orchestra. Use Mixcraft’s virtual instruments and virtual instrument tracks to demonstrate each instrument in the orchestra. Finally, attempt to compose a smaller melody for orchestra by using multiple virtual instruments.
FURTHER READING
Black, D. Essential Dictionary of Orchestra.
Levine, R. A Child’s Introduction to the Orchestra: Listen to 37 Selections While You Learn About the Instruments, the Music, and the Composers Who Wrote the Music!